Spasticity: Straub Tail Reaction
Discover how Melior’s unique phenotypic screening platforms can uncover the untapped value of your candidate therapeutic
Spasticity is defined as a muscle tone disorder characterized by hyperactive tonic stretch reflexes. To relieve abnormally increased muscle tone in patients suffering from painful muscle spasms, the centrally acting muscle relaxants are used (baclofen, tizanidine, mephenesin, memantine). Morphine-induced Straub tail reaction is expressed as a tonic dorsal extension of the tail and may reflect drug-induced transient spasticity. This test has been used to evaluate the effect of centrally acting muscle relaxants. We established the utility of the morphine-induced Straub test reaction for detecting potential anti-spasticity effects of compounds. The results point at the Straub tail response as a useful tool for in vivo screen of candidate compounds for CNS trauma and spasticity.
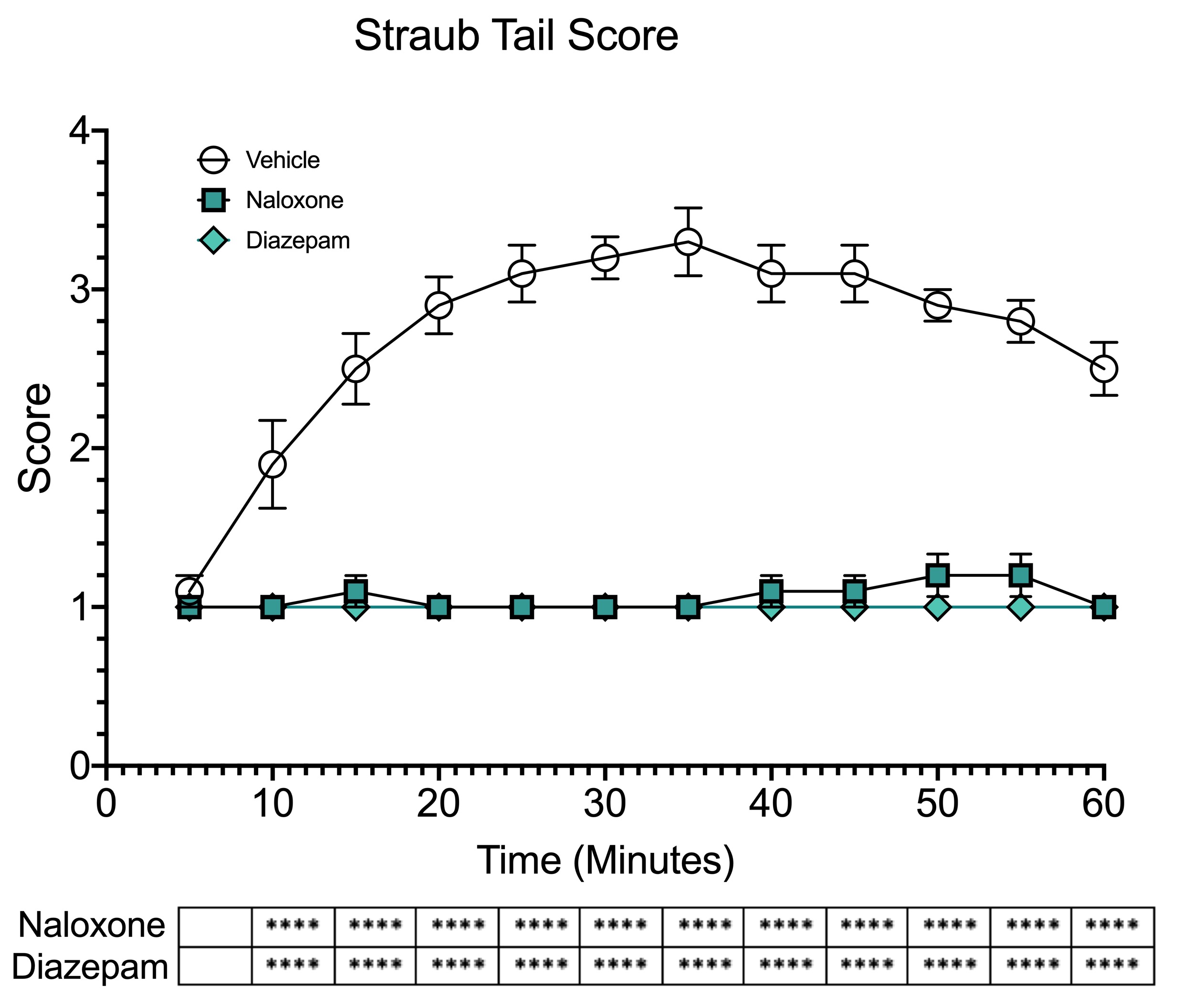
Straub tail score of naloxone (15 mg/kg SC) and diazepam (20 mg/kg PO) post morphine injection. The Straub tail score was taken every 5 minutes after injection of morphine (40 mg/kg SC). Scoring was performed as described by Belozertseva et al.,(2016). Significance at each time point is denoted in the graph below. Data are mean±SEM and analyzed by two-way ANOVA as applicable. (**** P<0.0001; compared to vehicle).
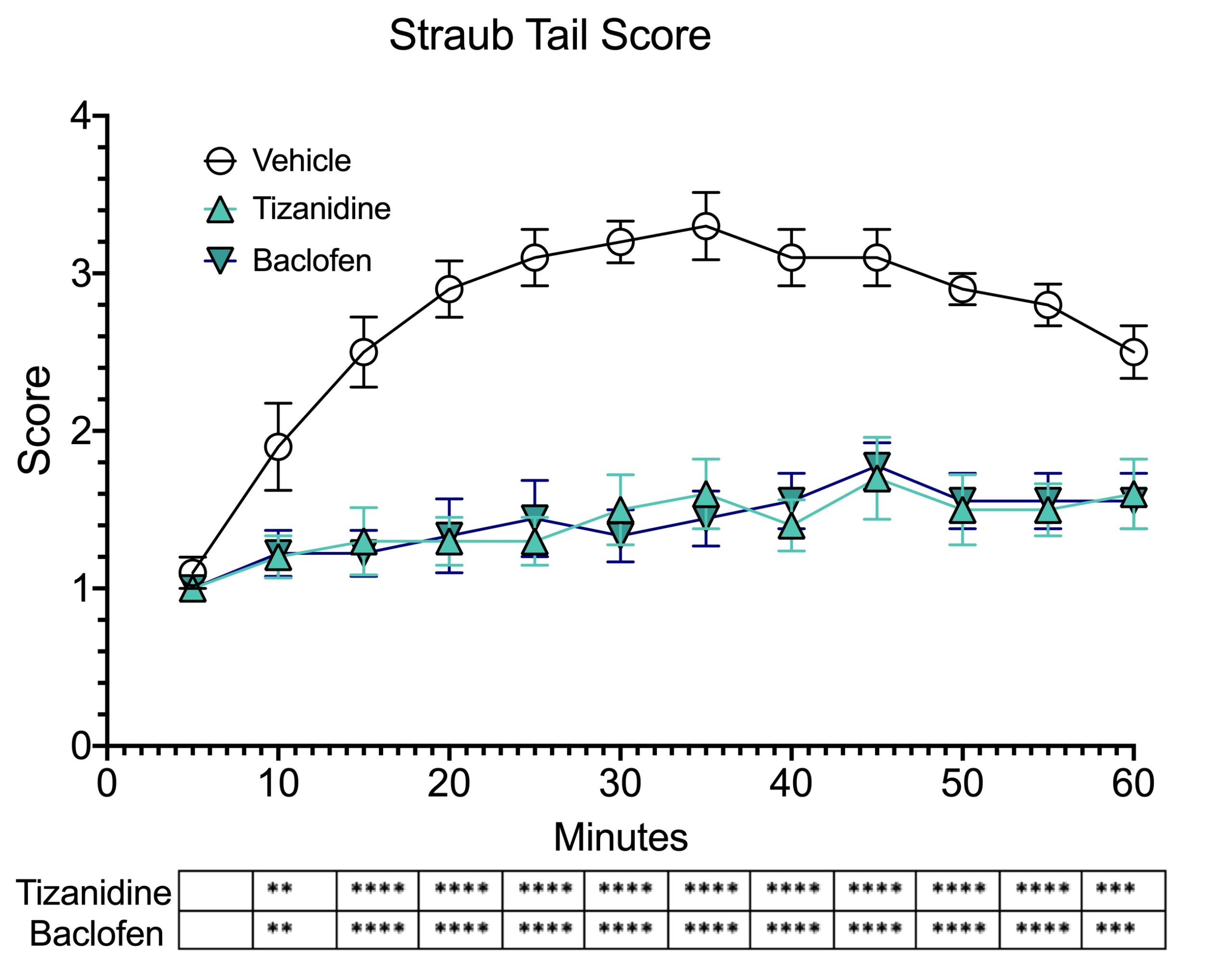
Straub tail score of tizanidine (3 mg/kg SC) and baclofen (10 mg/kg SC) post morphine injection. The Straub tail score was taken every 5 minutes after injection of morphine (40 mg/kg SC). Scoring was performed as described by Belozertseva et al.,(2016). Significance at each time point is denoted in the graph below. Data are mean±SEM and analyzed by two-way ANOVA as applicable. (**P<0.01;***P<0.001; **** P<0.0001; compared to vehicle).
Reference: Belozertseva et al. Morphine-induced Straub tail reaction in mice treated with serotonergic compounds. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 15;791:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.08.014. Epub 2016 Aug 24



 Interested in running a Straub Tail Test study?
Interested in running a Straub Tail Test study?