Irwin Test
Discover how Melior’s unique phenotypic screening platforms can uncover the untapped value of your candidate therapeutic
The Irwin test is an observational screening paradigm that is comprised of a battery of tests used to assess a mouse or rat’s neurobiological and physiological state. Parameters that are evaluated include autonomic and sensorimotor functions, convulsive behavior, and other activities produced by a drug after administration.
When conducted by an experienced tester the Irwin test can provide insight into a drug’s activity including potential molecular targets, therapeutic benefits and deleterious side-effects.
The Irwin test is used to identify subtle neurological perturbations produced by a drug and used to control for other behavioral and locomotor assays described in the Melior Discovery theraTRACE® platform. Although a behavioral test of sorts, it is not directed towards a specific indication.
The Irwin test is principally used by Melior to provide a context for other assays. This assay system will also be used during the pharmacokinetic and maximal tolerated dose preliminary studies to establish dose-response ranges for subsequent efficacy studies.
In the study summarized below, we assessed Diazepam, a centrally acting anxiolytic with some sedative activities in three different strains of mice: male CD1, male DBA1 and female SJL/J mice.
Mice were assessed for the features described below by two observers blinded to the treatment, 30 minutes after vehicle or Diazepam administration. Each parameter was scored on a 0 to 5 scale, with 0 representing the response in a normal animal and 5 representing a maximally impaired animal.
Ready to get started or looking for a custom model?
Contact us today for more information about our bespoke research models and to discuss how we can help you answer your unique research questions.
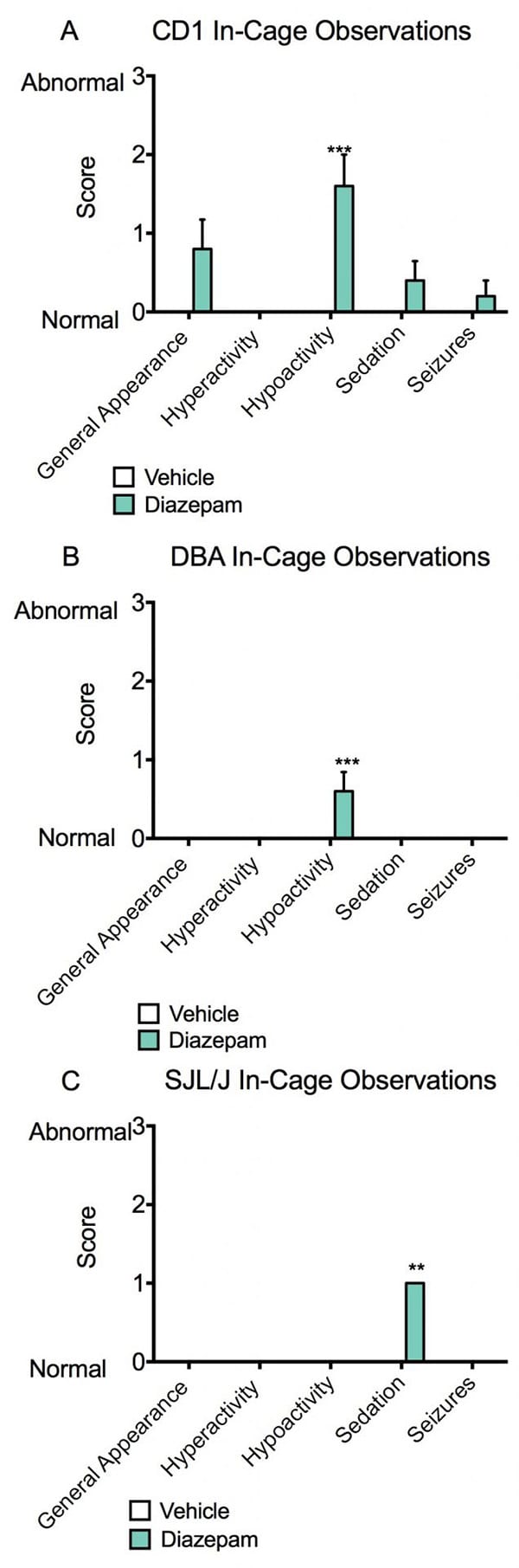
In cage observations and modified Irwin battery scores. Animals were dosed with vehicle or Diazepam 30 minutes prior to assessment. In cage observations include general appearance, hyperactivity, hypoactivity, sedation or seizure activity. Hypoactivity was significantly increased in Diazepam treated CD1 (A) and DBA1 (B) mice while sedation was significantly increased in Diazepam treated SJL/J mice. Data are mean ± SEM; **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 compared to vehicle.
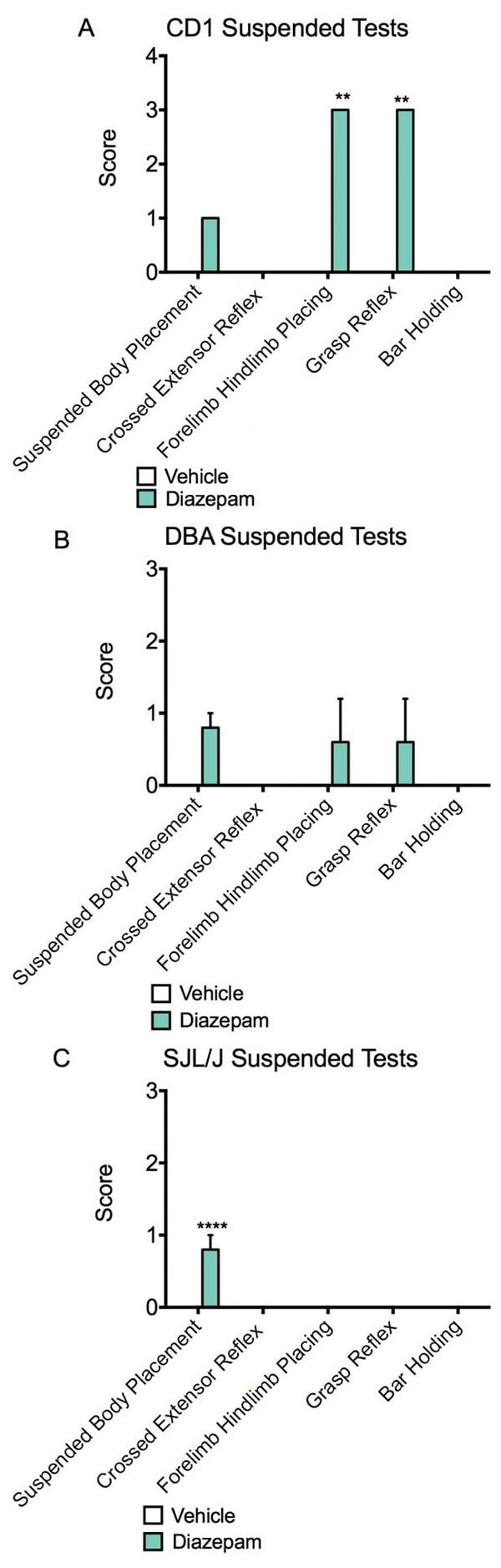
Suspended tests and modified Irwin battery scores. Animals were dosed with vehicle or Diazepam 30 minutes prior to assessment. Suspended tests include suspended body placement, crossed extensor reflex, forelimb hindlimb placing, grasp reflex and bar holding. Forelimb hindlimb placing and grasp reflex scores (A) were significantly increased in Diazepam treated CD1 mice and suspended body placement was significantly increased in Diazepam treated SJL/J mice (C). There were no significant changes in DBA1 mice (B). Data are mean ± SEM; **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001 compared to vehicle.
Autonomic responses and modified Irwin battery scores. Animals were dosed with vehicle or Diazepam 30 minutes prior to assessment. Autonomic response tests include righting reflex, tail pinch, auditory startle and defecation. In Diazepam treated mice, auditory startle and defecation were significantly increased in CD1 mice (A) and DBA1 mice (B). There were no significant differences in SJL/J treated mice, however an increased trend is present (C). Data are mean ± SEM; **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001 compared to vehicle.
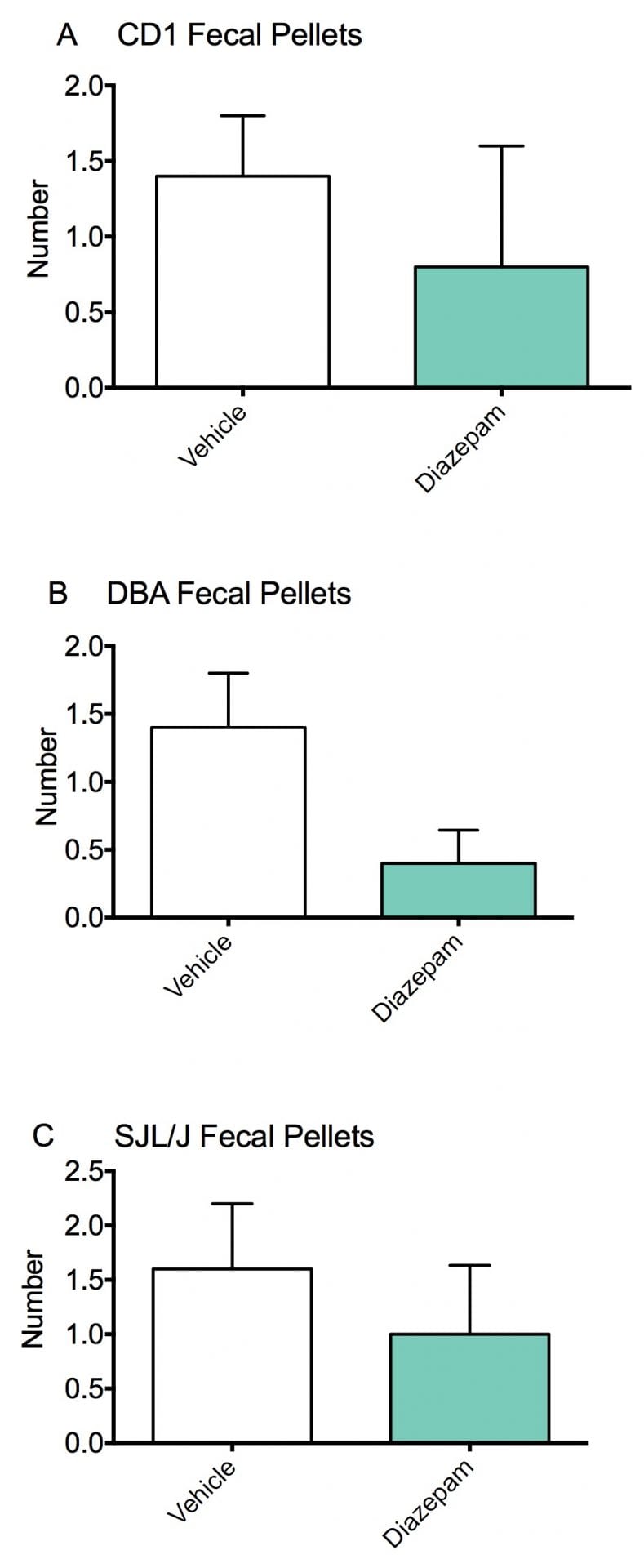
Fecal pellet production and modified Irwin battery scores. Animals were dosed with vehicle or Diazepam 30 minutes prior to assessment. There were no significant differences in fecal pellet production between all three groups (A-C). Data are mean ± SEM.
The Irwin functional observational battery is typically can be conducted in rats or mice. The variability is relatively low and statistical significance may be achieved with group sizes of about 8 to 10 animals. It can be performed in both mice and rats. Since it is non-invasive it can be easily incorporated several times over the course of a chronic study.
Frequently Asked Questions
Absolutely! An Irwin screening is non-invasive and can easily be performed in conjunction to other experiments.
A large variety of observations can be made at many timepoints. Undisturbed behavioral observations such as body position, locomotor activity, sedation, piloerection, writhing, jumping, tremors, twitching, and more. Other more invasive tests could be performed as a part of this umbrella test, including forelimb hindlimb placing, grasp reflex, tail pinch, righting reflex, auditory startle, and more. The advantage of the Irwin tests, is the customizability.
Generally, we can start a study within 2 weeks notice.
Synonyms: rodent observational battery, rodent neurological battery



 Interested in running the Irwin Test?
Interested in running the Irwin Test?