EMT-6 Syngeneic Breast Tumor Model
Test novel breast cancer therapies and advance immuno-oncology research with EMT-6 syngeneic models.
Breast cancer is a widespread disease affecting millions of women worldwide. Between 2015 and 2020, an estimated 7.8 million women were diagnosed with breast cancer.
When you partner with Melior, you can leverage the EMT-6 syngeneic breast cancer mouse model to test novel therapies, evaluate their efficacy, and ultimately accelerate the development of effective immunotherapies for breast cancer.
Melior Discovery’s EMT-6 tumor models:
- Current breast cancer treatment landscape
- About the EMT-6 tumor model
- EMT-6 tumor model specifications
- Custom services and tools: How to enhance your research
- Immuno-theraTRACEⓇ platform
- Explore validated models through data highlights
Current Breast Cancer Treatment Landscape
The primary treatments for breast cancer are surgery and radiation. Hormone receptor-positive receptor or HER2-positive breast cancers (80-85%) also have various pharmacological approaches to combat the disease. Tumors that are estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2 negative (triple negative breast cancer or TNBC) have limited treatment options and a more dire prognosis. Despite this, TNBC can still be responsive to chemotherapeutic approaches, and to a lesser extent, immunotherapy approaches such as checkpoint inhibition.
Due to high incidences and a significant proportion of refractory tumor types, improved pharmacological treatments for certain types of breast cancer are a medical necessity.
Melior’s breast cancer mouse models are an important tool to support scientists in achieving this goal.
Accelerate Your Immunotherapy Research with the EMT-6 Syngeneic Model
We developed our EMT-6 tumor model from murine mammary carcinoma derived from a transplanted hyperplastic alveolar nodule from a BALB/c mouse. This model can also investigate cytotoxic therapeutic candidates and immune-modulating agents such as checkpoint inhibitors. We developed the EMT-6 syngeneic breast cancer mouse model to complement our xenograft breast cancer model, which uses the human MCF-7 cell line.
The EMT-6 tumor model has a high frequency of tumor production with consistent growth rates. The model has been shown to respond to immune checkpoint inhibitors, making it a valuable tool for studying immunotherapies. With its ability to reliably reproduce human disease characteristics, the EMT-6 syngeneic model is an invaluable tool for preclinical research in breast cancer. It has begun to pave the way for the development of new and effective treatments for this devastating disease.
Maximize Your Preclinical Success with EMT-6 Tumor Models for Breast Cancer
The EMT-6 syngeneic breast cancer mouse model offers several key benefits for preclinical drug development. These include:
- Set up as subcutaneous or orthotopic (in mammary fat pad; MFP)
- High tumor take rate and consistent tumor growth rates
- Responsiveness to various immunotherapies, including immune checkpoint inhibitors
- Mimics the human tumor microenvironment, allowing for more accurate preclinical research
- Cost-effective compared to other preclinical models
- Can be used to test the efficacy of new immuno-oncology treatments and to evaluate the effectiveness of novel combination therapies
Optimize Your Study Results with Tailored Tools and Services
Get the most out of your study by integrating custom services and analyses. We help design your study and select the appropriate analytical endpoints to maximize your results.
Some of our services include:
- Tissue collection for immune cell analysis and profiling
- Whole blood, spleen, and lymph node analysis
- General observations, including pain analysis
- Histology and IHC
- Luciferase assays
- IVIS imaging
- FACS analysis
- PK studies
Don’t see what you’re looking for? Contact us for a comprehensive list of services.
Expand your applications with Immuno-theraTRACEⓇ
With our oncology platform, Immuno-theraTRACEⓇ, you can simultaneously test your immunotherapeutic in 8 syngeneic models. This helps you determine the best target cancer type to advance your immunotherapy.
In addition to testing your drug in our EMT-6 tumor model, Immuno-theraTRACEⓇ, lets you simultaneously analyze your immunotherapies in 7 other tumor types and get results in 8 just weeks.
Data highlights: Implantation method responses to immunotherapies
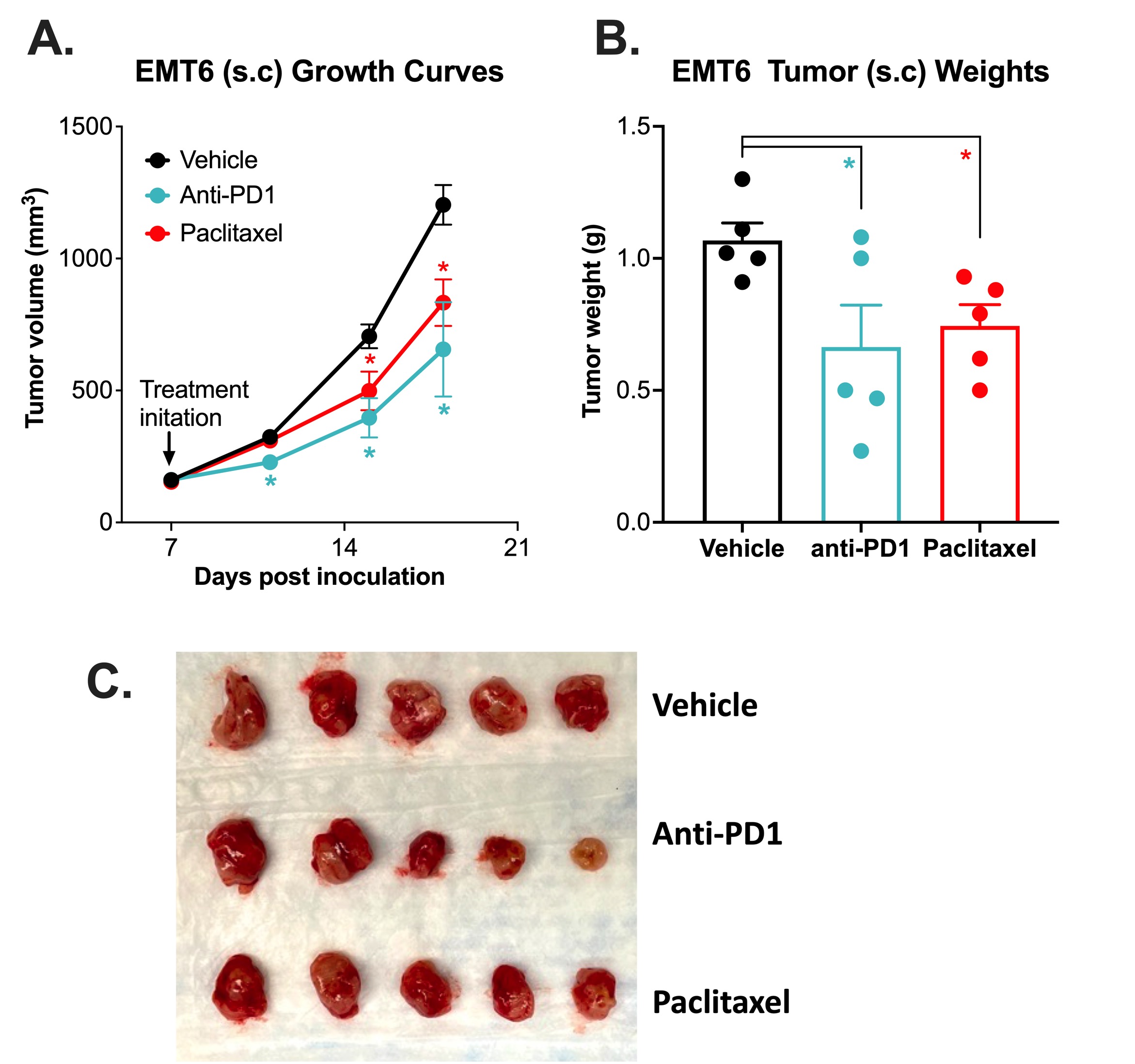
Subcutaneous Breast EMT-6 Syngeneic Model with Anti-PD1 and Paclitaxel
Immune checkpoint inhibitor and chemotherapy validation of a subcutaneous mouse EMT-6 syngeneic model.
The EMT-6 tumor model was created by injecting 1 x106 EMT-6 cells into the rear flank of Balb/c mice. Once the tumor size reached ~150mm3 (Day 7), mice were randomized into groups and treated with vehicle, anti-PD-1 antibody (12.5mg/kg, IP twice per week), or paclitaxel (20 mg/kg, IP once per week). Tumor volume was monitored twice per week using calipers (A). At the end of the study (Day 18), animals were sacrificed, tumors were excised and weighed (B, C). Data area mean ± SEM. n=5/group. Data are mean ±SEM. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01 by Student’s t-test
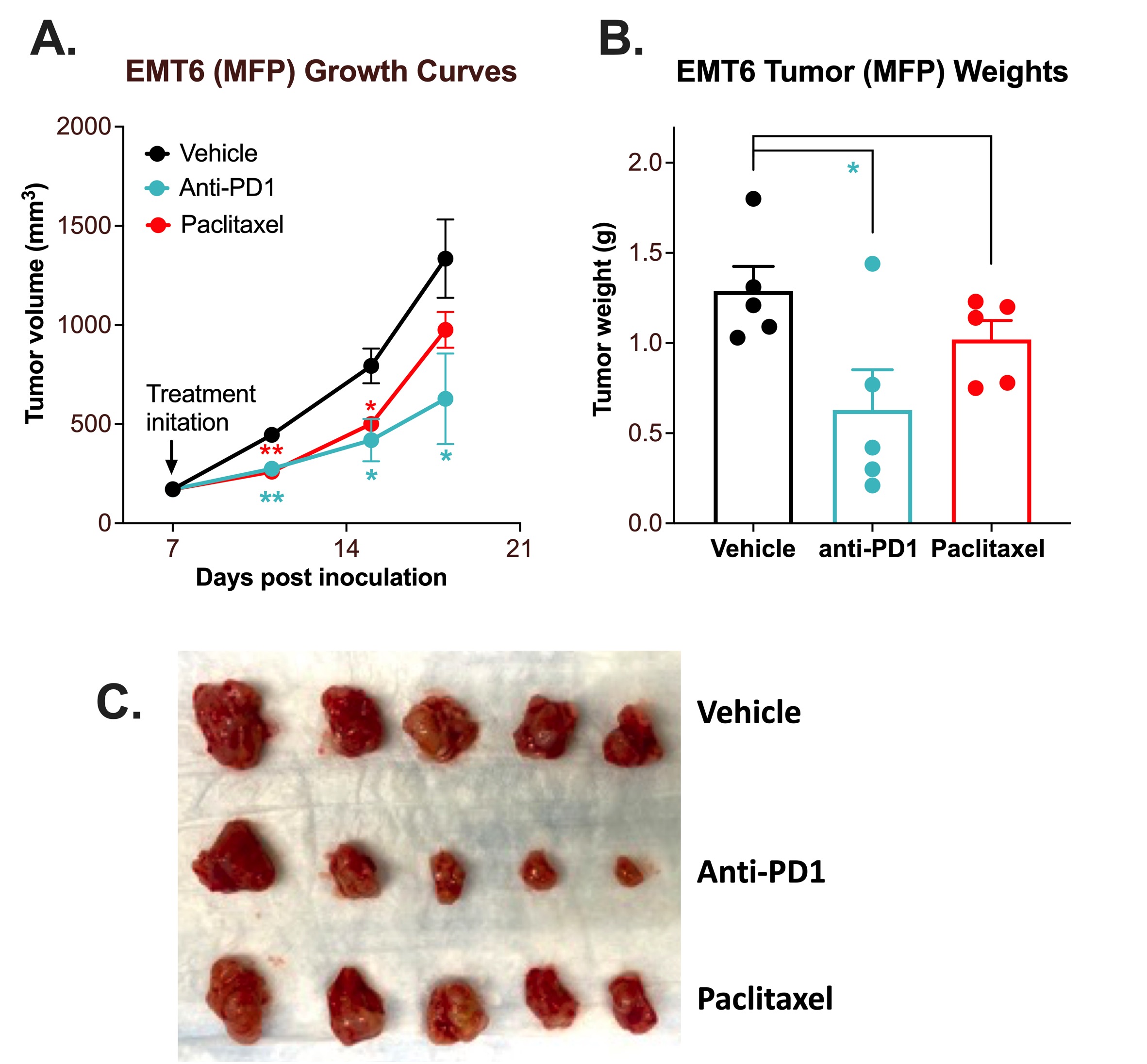
MFP Breast EMT-6 Syngeneic Model with Anti-PD1 and Paclitaxel
Immune checkpoint inhibitor and chemotherapy validation of an orthotopic mouse EMT-6 syngeneic model.
The EMT-6 tumor model was created by injecting 1 x106 EMT-6 cells into the lower right mammary fat pad (MFP) of Balb/c mice. Once the tumor size reached ~100mm3 (Day 7), mice were randomized into groups and treated with vehicle, anti-PD-1 antibody (12.5mg/kg, IP twice per week), or paclitaxel (20 mg/kg, IP once per week). Tumor volume was monitored twice per week using calipers (A). At the end of the study (Day 18), animals were sacrificed, tumors were excised and weighed (B, C). Data area mean ± SEM. n=5/group. Data are mean ± SEM. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01 *** P<0.001 by Student’s t-test
Melior can initiate your EMT-6 tumor model study with short lead times and with a bespoke study design to suit your needs. Including time to establish tumor-bearing mice (1-2 weeks) and typical treatment times (2 weeks) these studies normally run for approximately 4 weeks. The mouse EMT-6 syngeneic model also yields highly reproducible tumor growth curves with small error bars capable of detecting changes in growth rates with relatively small group sizes.
Are you ready to transform the landscape of breast cancer treatment?
Citations
- Breast cancer. Accessed April 14, 2023.
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer



 Interested in running an EMT-6 tumor model study?
Interested in running an EMT-6 tumor model study?